One of the main requirements for 5G to be usable in Industry 4.0 scenarios is that it must be able to replicate the deterministic and low-latency nature of communication that would be expected as in case of wired networking.
Last year, Devaki Chandramouli, Work Item Rapporteur at 3GPP, wrote an article titled, '5G for Industry 4.0'. Quoting from the article:
In order to be able to deploy 5G for new and diverse use cases, including industry 4.0 and factory automation, the 5G system must work in harmony with the communications technologies used in such industries. For this purpose, 3GPP has now made significant progress towards the integration of the 5G system with IEEE 802.1 working group specifications covering Time Sensitive Networking (TSN).
The ‘Vertical_LAN’ work item, in 3GPP Release-16, introduces the following three new and distinct 5G enablers for Industry 4.0;
- Support for Time Sensitive Communications by seamlessly integrating the 5G system as a bridge to IEEE TSN.
- Support for Non-Public Networks.
- Support for a 5G-LAN type service.
The IEEE TSN set of specifications is considered the convergence technology that will enable deterministic and low-latency communication in the factories of the future. 5G Time Sensitive Communication is a service that supports deterministic and/or isochronous communication with high reliability and availability. It provides packet transport with Quality of Service (QoS) characteristics such as bounded latency and reliability, where end systems and relay/transmit nodes can be strictly synchronized.
3GPP supports TSN time synchronization, by considering the entire end-to-end 5G system as an IEEE 802.1AS "time-aware system". Only the TSN Translators (TTs) at the edges of the 5G system need to support the IEEE 802.1AS operations. UE, gNB, UPF, NW-TT and DS-TTs are synchronized with the 5G GM (i.e. the 5G internal system clock) which keeps these network elements synchronized.
The TSN Translators fulfil all functions related to IEEE 802.1AS. Furthermore, time sensitive communications (TSC) assistance information has been introduced to provide the deterministic traffic pattern to the 5G RAN and to facilitate optimized scheduling of time sensitive traffic.
5G LAN-type Service
5G LAN-type service provides services with similar functionalities to Local Area Networks (LANs) and VPN’s but improved with 5G capabilities (e.g., high performance, long distance access, mobility and security). The 5G LAN type service enables management of 5G Virtual Network (VN) Group identification, membership and group data. The 5G VN Group management can be configured by a network administrator or can be managed dynamically by third party apps (AF).
In order to support dynamic management of 5G VN Group identification and membership, the NEF exposes a set of services to manage (e.g. add/delete/modify) the 5G VN group and 5G VN member.
The NEF (Network Exposure Function) also exposes services to dynamically manage 5G VN group data. Furthermore, 5GS supports optimized routing by enabling support for local switching at the UPF without having to traverse the data network for UE-UE communication when the two UE(s) are served by the same User Plane Function.
You can read the complete article on 3GPP's website here.
I haven't yet managed to find a simple tutorial on TSN yet. The 3GPP article is simple enough.
A talk titled, 'Wireless Time Sensitive Network (TSN) – From Ethernet to WI-FI, 5G and beyond' by Dave Cavalcanti, Principal Engineer, Intel Corporation at IEEE Comsoc Oregon chapter is a good place to start. Video is available on YouTube here.
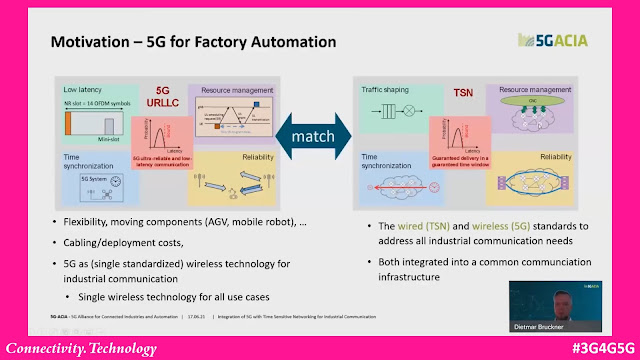
A 5G-ACIA Web Seminar, 'Integration of 5G with Time Sensitive Networking for Industrial Communications' looks at this topic from Industrial 5G perspective. The webinar is embedded as follows:
A 5G-ACIA whitepaper with the same name is also available here. The white paper has good amount of details and describes and examines integration of 5G with TSN for typical industrial use cases, namely controller-to-controller, controller-to-device and device-to-compute communications. It shows that 5G, as specified in 3GPP Release 16 and 17, provides all functionality needed for integration with TSN for industrial automation.
Related Posts:
- 3G4G: Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-2-Machine (M2M)
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Industrial 5G – for the industry of tomorrow
- Free 6G Training: Do vertical industries really need 6G?
- The 3G4G Blog: 5G and Industry 4.0
- The 3G4G Blog: What is Industrial IoT (IIoT) and how is it different from IoT?
- The 3G4G Blog: Challenges and Future Perspectives of Industrial 5G
- The 3G4G Blog: 5G Private and Non-Public Network (NPN)
- The 3G4G Blog: '5G RAN Release 18 for Industry Verticals' Webinar Highlights
- The 3G4G Blog: Introduction to 5G Reduced Capability (RedCap) Devices
- Connectivity Technology Blog: Cellular Connectivity Technology Landscape and Standards for Industrial IoT

Comments
Post a Comment